 |
| Law of mass action Or Law of equilibrium |
Law of mass action Or Law of equilibrium
Introduction: The effect of concentration in reversible reaction at
equilibrium was discovered by two Norwegian chemists. C.M Guldberg and P. Waage
in since 1864.They studied about the relation of dynamic equilibrium between
the concentrations of different species. So, their observation for the concentration
of different species in reversible reaction at dynamic equilibrium is known as
a law of mass action or law of equilibrium.
Statement: This law states that
“The rate of a chemical reaction is directly
proportional to the product of active masses (concentration) of reactants at
constant temperature”.
Active Masses: The
representation of concentration of reactants and products in mole / dm3 or mole dm –3 or in mole / litre is called active masses.
The concentration of these species are expressed in square bracket [ ]. Which
shows the molar concentration.
Derivation of expression for equilibrium Constant
Consider a reversible reaction in which reactants A + B react
to form C + D and the product C + D react to form the reactants A + B.
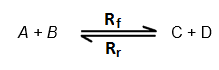
Where Rf shows forward reaction and Rr
shows the reverse reaction.
According to law of
mass action we came to know this
1.
Rate
of forward reaction (RF) ∝ [A][B]
Rate
of forward reaction (RF) = Kf[A][B]
2.
Rate
of reverse reaction (Rr) ∝ [C] [D]
Rate
of forward reaction (Rr) = Kr[C] [D]
Where Kf and
Kr are proportionality constant. And at the
dynamic equilibrium both forward and reverse reaction are equal. That is Rf= Rr
Related posts
Related posts
At chemical equilibrium state Or dynamic equilibrium state
As
we know that
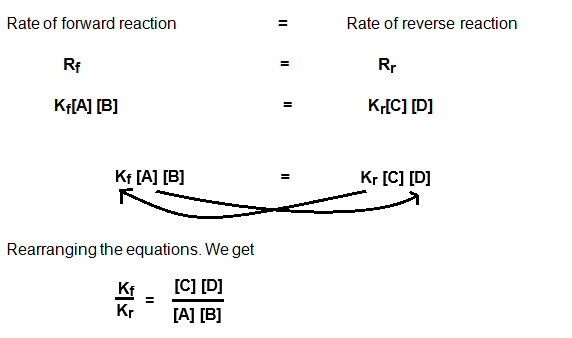
Where both Kf and Kr are constant. So, combined them to get one single constant.
That is
Where K shows equilibrium constant and C shows the molar concentration. For
more explanation
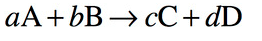
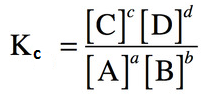
According to the gaseous system

Where p is the partial pressure
of any gaseous system and Kp represents equilibrium constant for gaseous system. Where
concentration is measured by using partial pressure of gases.
Partial Pressure:The
pressure exerted by an individual gas in a gaseous mixture is called partial
pressure of gas and is denoted by P.



